Membrane Transport Proteins
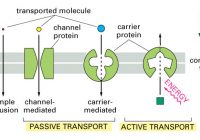
Membrane Transport Proteins Part A What distinguishes facilitated diffusion from simple diffusion? No energy is used to move molecules across the membrane. Membrane proteins help move molecules across the membrane. Molecules move from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Molecules move from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration.… Read More »