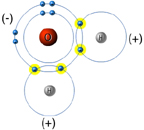
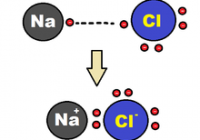
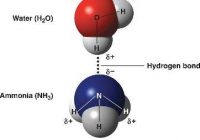
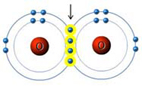
Ocean Acidification
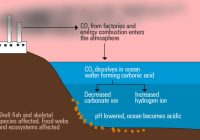
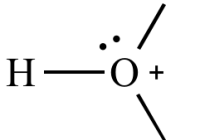
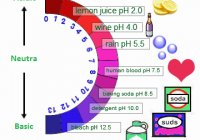
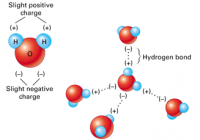
Ocean Acidification Part A What is the main reason that the oceans are becoming more acidic? the dumping of garbage and sewage into the oceans absorption by the oceans of carbon dioxide generated by burning fossil fuels large crude oil spills in the oceans fertilizer runoff in major rivers flowing into the oceans Correct Part B How much… Read More »